If you’re working in technology you’ll know that our world is full of metrics, acronyms and jargon. Especially when it comes to metrics.
This post helps to demystify those three-letter terms that get thrown around the tech world in sales, marketing and finance and how they can help measure success.
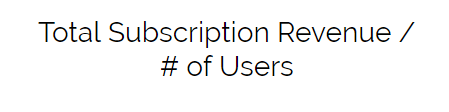
ARPU – Average Revenue Per User
CAC – Customer Acquisition Cost
CPA – Cost Per Action
CPC – Cost Per Click
CPM – Cost Per Mille
CTA – Call To Action
CTR – Click Through Rate
EDM – Electronic Direct Mail
GTM – Go To Market
KPI – Key Performance Indicators
MAC – Marketing Acquisition Cost
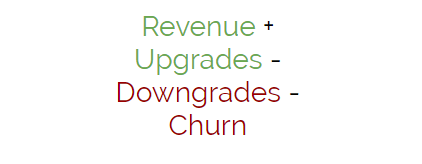
MRR – Monthly Recurring Revenue
MQL – Marketing Qualified Lead
NPS – Net Promoter Score
SAC – Sales Acquisition Cost
SQL – Sales Qualified Lead
TAM – Total Addressable Market
ARPU – Average Revenue Per User
This is the average revenue across your customers/users. It’s calculated by taking subscription revenue and dividing by the user count. This metric can help evaluate which plans your users prefer. If the number is low, you will need more customers to keep afloat. Consider strategies to upsell to the next plan, or offer add-on products.
Use this in conjunction with Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) to find the time period in which you can recoup your costs.
CAC – Customer Acquisition Cost
The average cost of acquiring a new customer/user. Calculated by dividing all sales and marketing costs by the number of new users adding during the period. If your costs to acquire a customer is higher than the value they are bringing, something needs to change.
- Optimise your website so it is easy for trialists to convert to paying with little interaction from salespeople.
- Use a lead score model to determine which leads do need some human interaction. Leave those who would convert with little help to do it themselves.
- Use referral codes for friends and colleagues to invite new users. This requires little investment and word-of-mouth marketing is more authentic than traditional advertising.
CPA – Cost Per Action
A concept relating to paid digital advertising. The advertiser only pays when the user sees the ad, clicks the ad, and performs a set action on the website such as clicking a signup button.
CPC – Cost Per Click
A concept relating to Paid Digital Advertising. The advertiser only pays when the user sees the ad and clicks the ad. This is a useful way to measure engagement as users have to not only see your ad but have to do something about it.
CPM – Cost Per Mille
A concept relating to paid digital advertising. The advertiser only pays per thousand (mille is Latin for ‘thousand’) impressions of an ad. The strategy makes sense if you are advertising something highly specialised or are looking to build awareness of your product.
CTA – Call To Action
What the marketing or digital team want the user to do at the end of an email or on a landing page. Usually, a prompt to click a button, sign up, log in or perform an action in the product.
CTR – Click Through Rate
A concept relating to paid digital advertising and email marketing. Calculated by dividing the number of clicks by the total population, whether that is in an email or on a webpage.
In email marketing, the CTR is the better metric than the open rate when looking at the success of a campaign. Readers may want to unsubscribe or are simply opening the email to see what it is, then delete it.
EDM – Electronic Direct Mail
The electronic version of direct mail. Marketing messages which land in your users’ inbox.
GTM – Go To Market
The sales and marketing teams who produce a comprehensive list of things that need to be done when launching a new feature or product, including things to consider before, on and after launch.
KPI – Key Performance Indicators
A way that businesses measure their success. This can be a set of goals or metrics that the business strives to meet over a period of time.
MAC – Marketing Acquisition Cost
The average cost of acquiring a new customer/user. Calculated by dividing all marketing costs by the number of new users adding during the period.
MRR – Monthly Recurring Revenue
Calculated by adding together subscription revenue, upgrades from existing customers and subtracting downgrades and churn. An essential metric if your product is subscription-based. Answers the question “How much money would we get if we billed all our customers right now, assuming all their discount periods have expired?”
MQL – Marketing Qualified Lead
A user who has interacted with the website or with emails showing that they are a potential new user. Marketing then nurtures this user with targeted content across multiple platforms until they become a Sales Qualified Lead.
NPS – Net Promoter Score
Used in customer research to determine if a user is a detractor, passive or promoter of your product or organisation.
Questions in these surveys relate to how likely a user is to recommend your business to a friend and how the experience with your product or website could be improved.
SAC – Sales Acquisition Cost
The average cost of acquiring a new customer/user. Calculated by dividing all sales costs by the number of new users adding during the period.
SQL – Sales Qualified Lead
A lead who has show indications that they are ready to buy, like taking out a free trial. They are then ready for a sales call to close the deal.
TAM – Total Addressable Market
The total value of all users in a given industry or location. Calculated by investigating how many customers are in the industry or location and multiplying by the subscription fee.
These are just some of the metrics that measures that are used in the SaaS business across finance, sales and marketing. Depending on your business there may be more KPIs that indicate how you are doing.
However, metrics are useless if they don’t lead meaningful insights and recommendations. The important thing to remember is that more metrics are not necessarily better and not too stay fixated on the numbers.
Photo by Matthias Groeneveld from Pexels

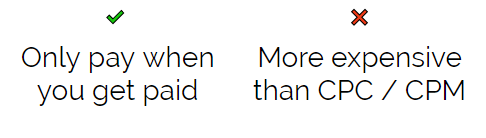






Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.